Permeable reactive barrier (PRB)
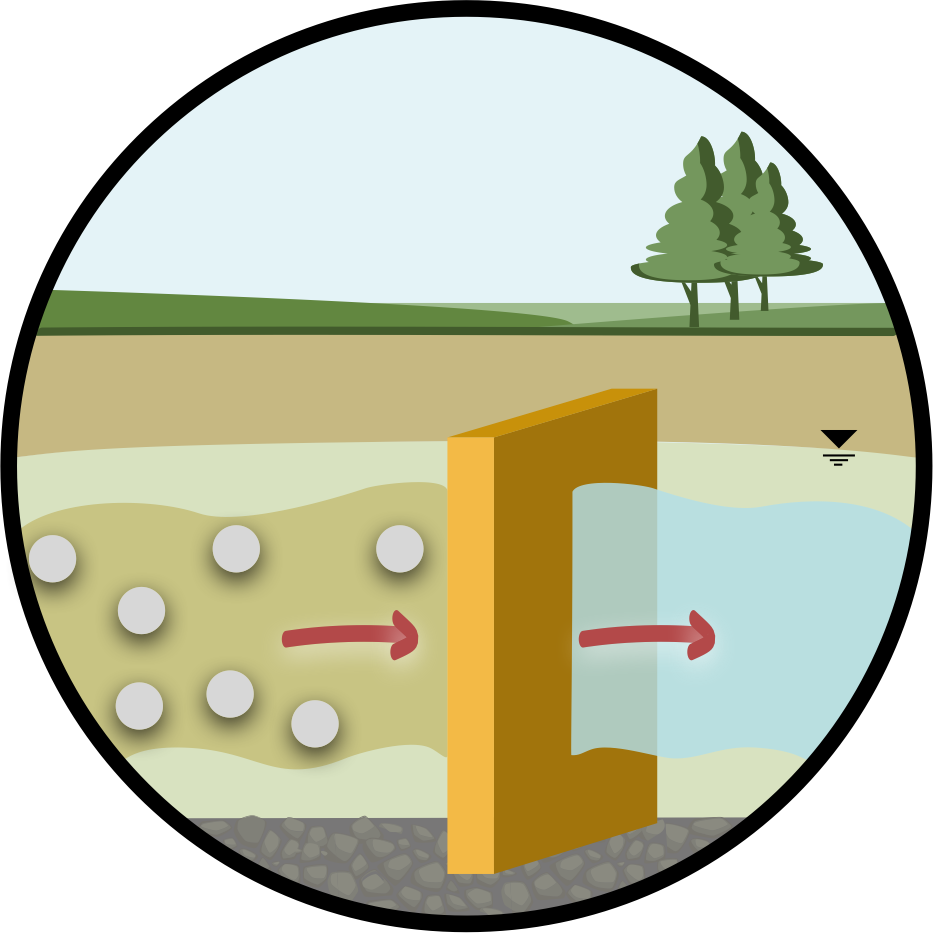
- Passive remediation of spreading groundwater pollution
- Highly modular and cost effective
- Effective against organic and inorganic contaminants
- Sequential remedial actions are possible when facing multi-contaminant plumes
- Soft soils
- Non-cohesive soils
- High-moisture soils
- Can treat soils up to 30 m (from surface)
- Can be installed using excavators, soil mixing, or injection rigs
- Can be combined with cut-off walls in a “Funnel and Gate” system
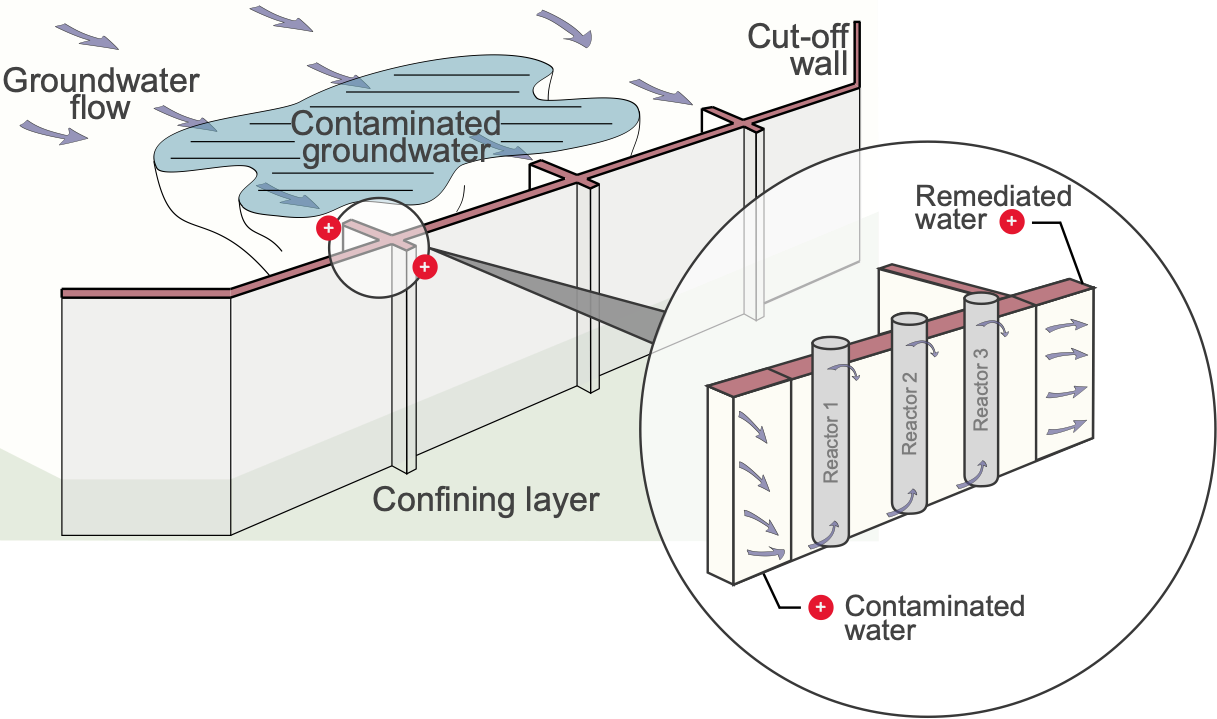
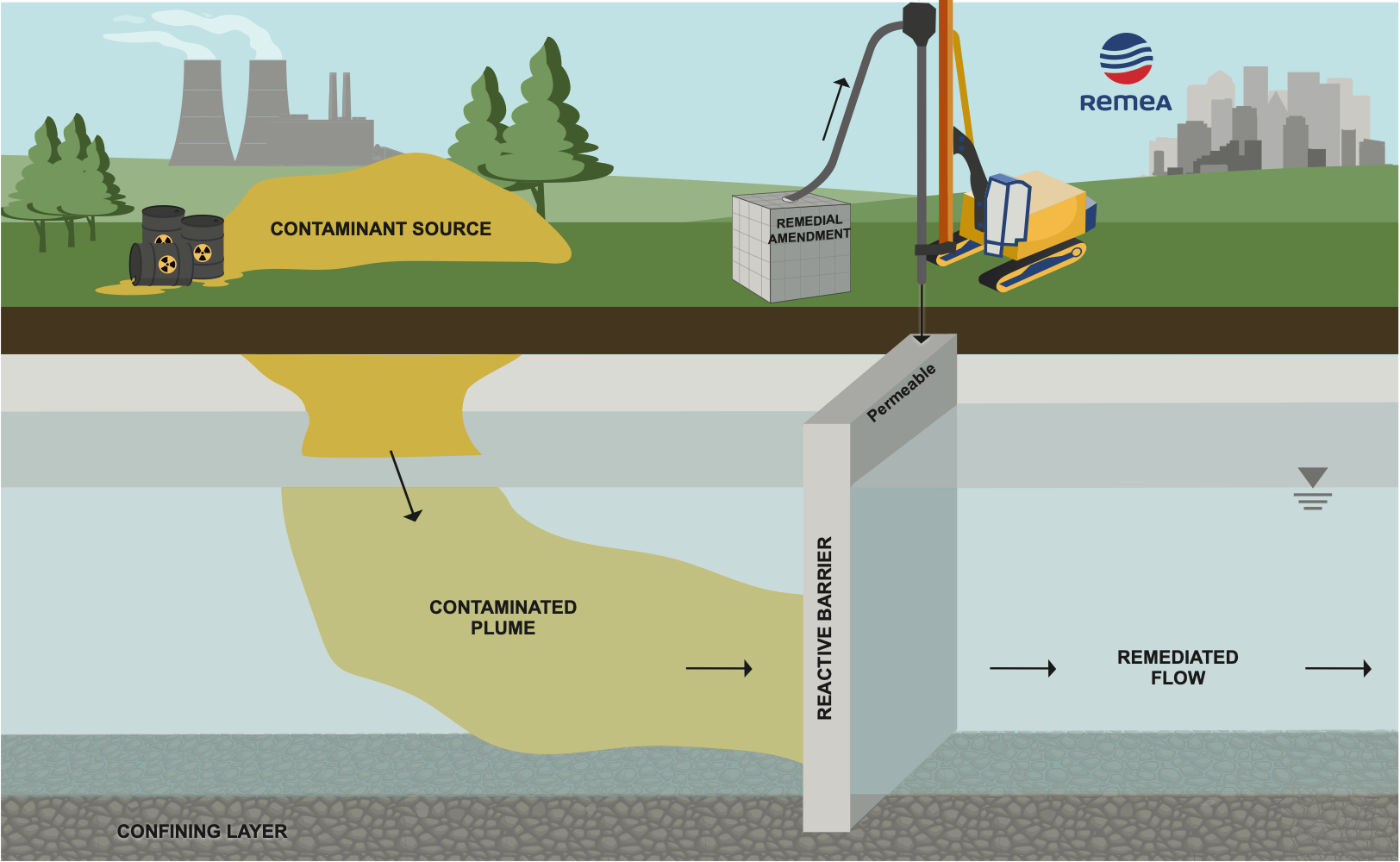
A Permeable Reactive Barrier (PRB) is a type of in-situ remediation technology used to intercept and treat contaminated groundwater as it flows through the reactive material. Depending on the site, this technique is usually combined with a mass treatment method to remediate contaminant source(s).
Installation process
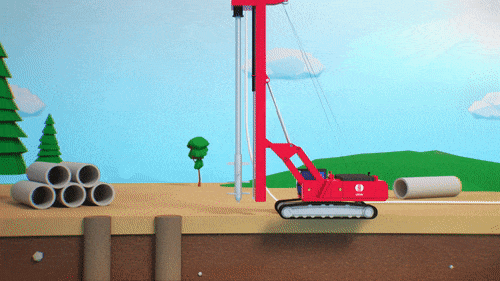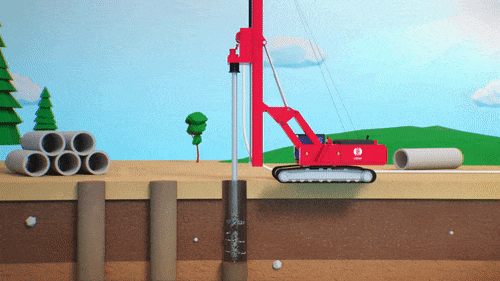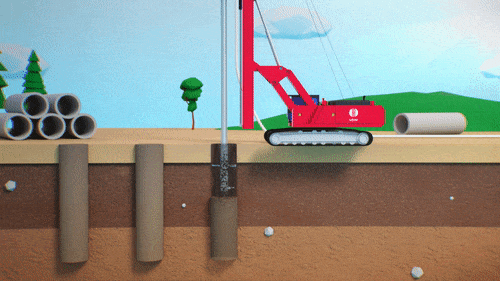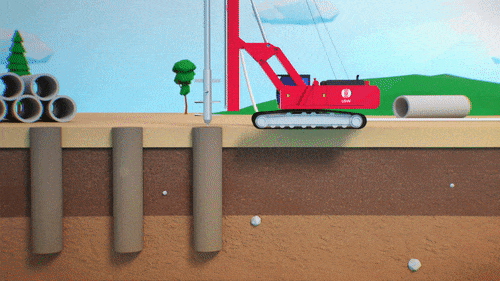
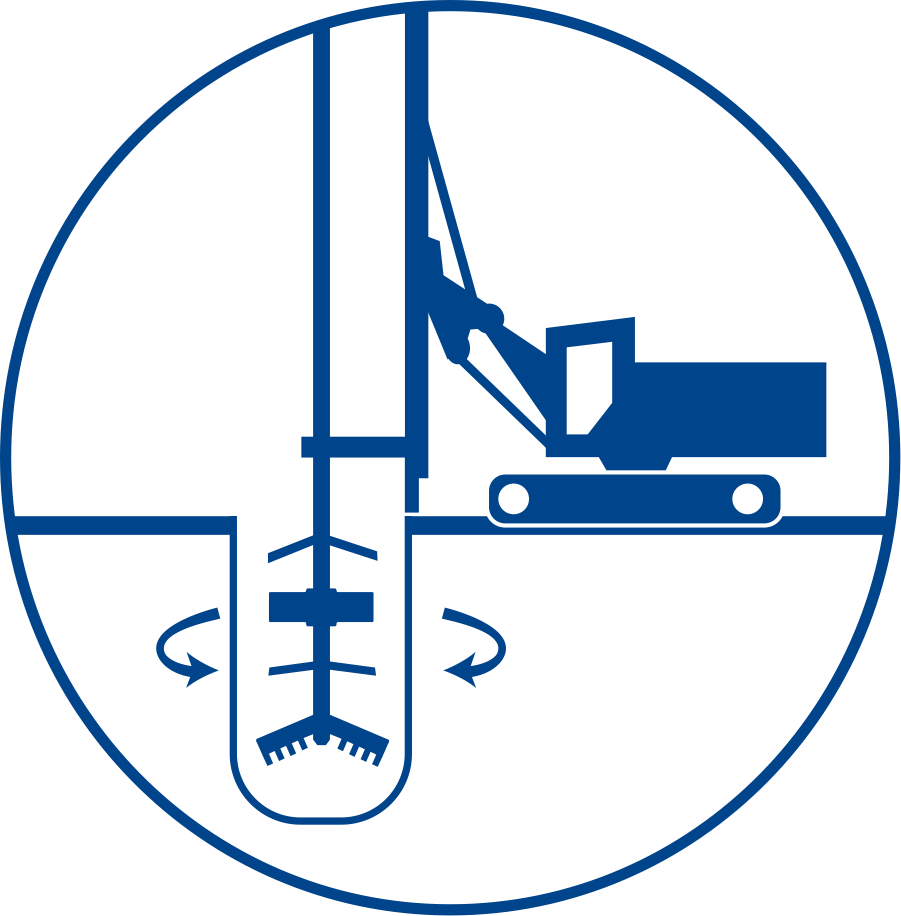
The reactive material is usually placed downstream of the pollution source and can be installed using injection, excavation, or physical mixing. The selected method will depend on i) site conditions, ii) type of contaminants, iii) regulatory requirements, and on iv) whether or not Excess Soils can be generated.
When working on historically contaminated sites, it is vital to properly delineate pollution spread so that we may optimize PRB size and location to the specifics of that site.
Grid pattern options
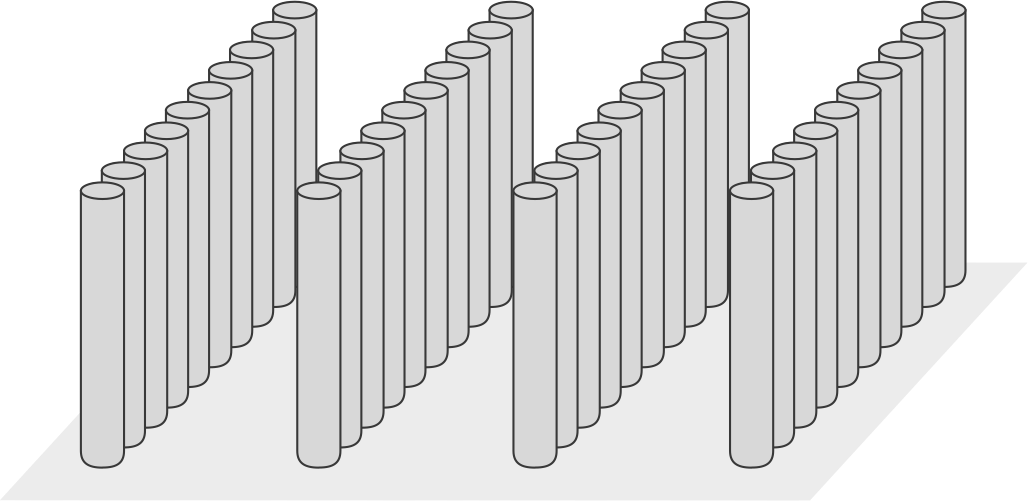
Wall-type
Downstream wall-type installations are typically the only grid pattern used when installing a PRB on a contaminated site.
Applications for classic PRBs
PRBs are used to remediate groundwater from organic or inorganic pollutants. Pollutant removal strategies include i) immobilization using sorption and precipitation strategies, ii) chemical transformations, and iii) biological transformations. As illustrated, all three remediation strategies can be sequentially combined when plumes contain a multitude of contaminants.
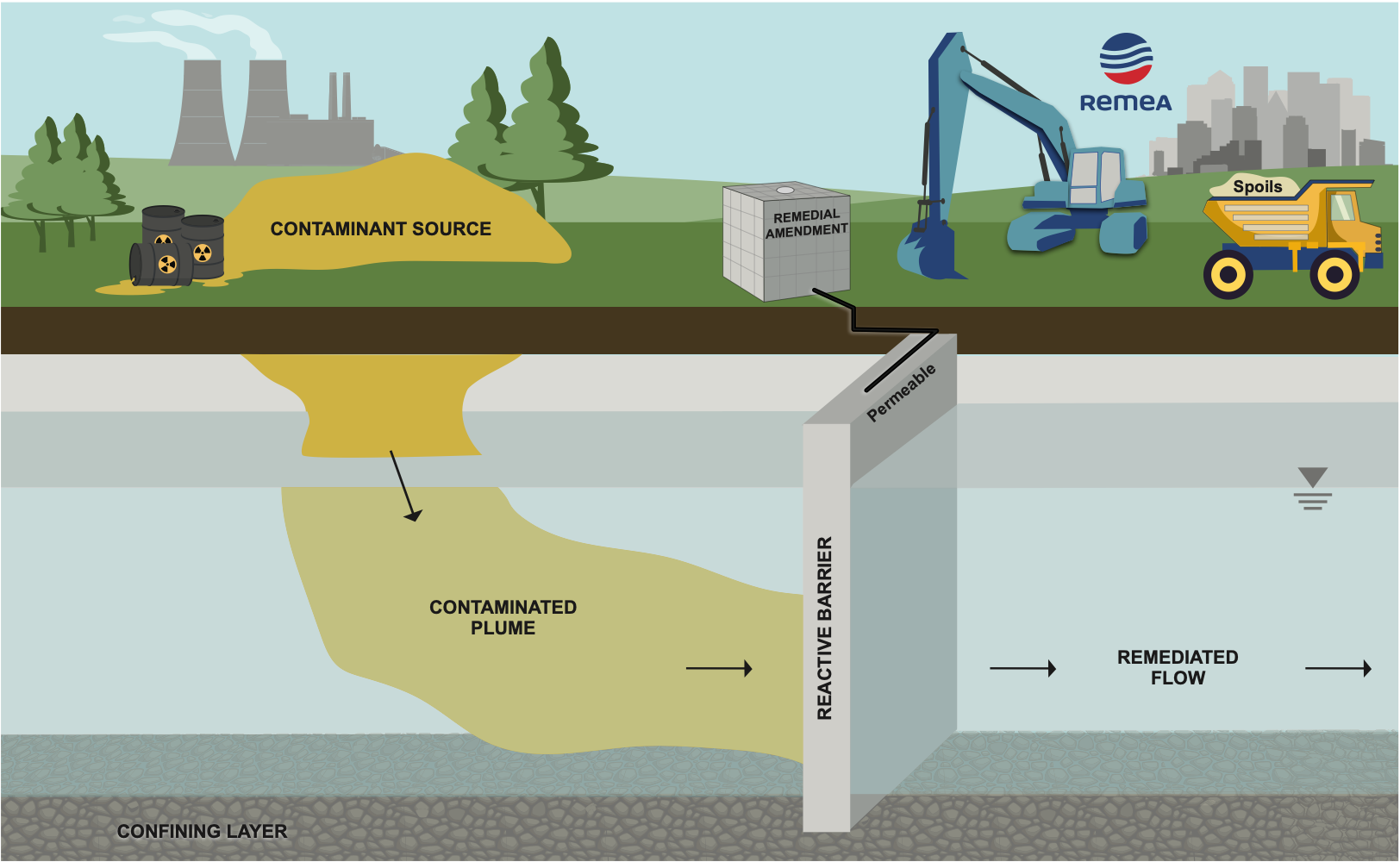
Depending on the specifics of each site, we can also install PRBs using excavators.
Serviceable PRBs