Groundwater cut-off walls
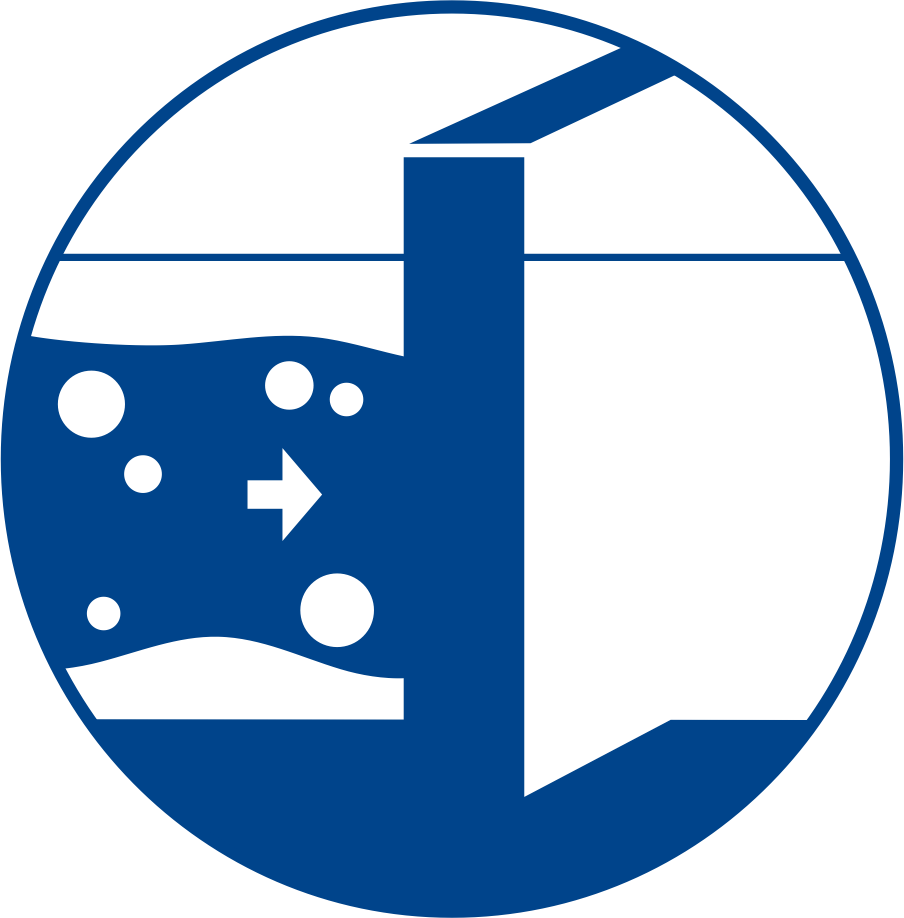
- Used to redirect, contain, capture or to prevent contaminants from spreading to undesirable locations.
- Can be rapidly implemented to contain contaminants close to the source or to redirect contaminants to a desired location.
- Can be combined with a chamber system to remediate groundwater.
- Soft soils
- Non-cohesive soils
- High-moisture soils
- Can be installed on confining layer up to 30 m (from surface)
- Both soil mixing rigs and large boom excavators can be used to implement.
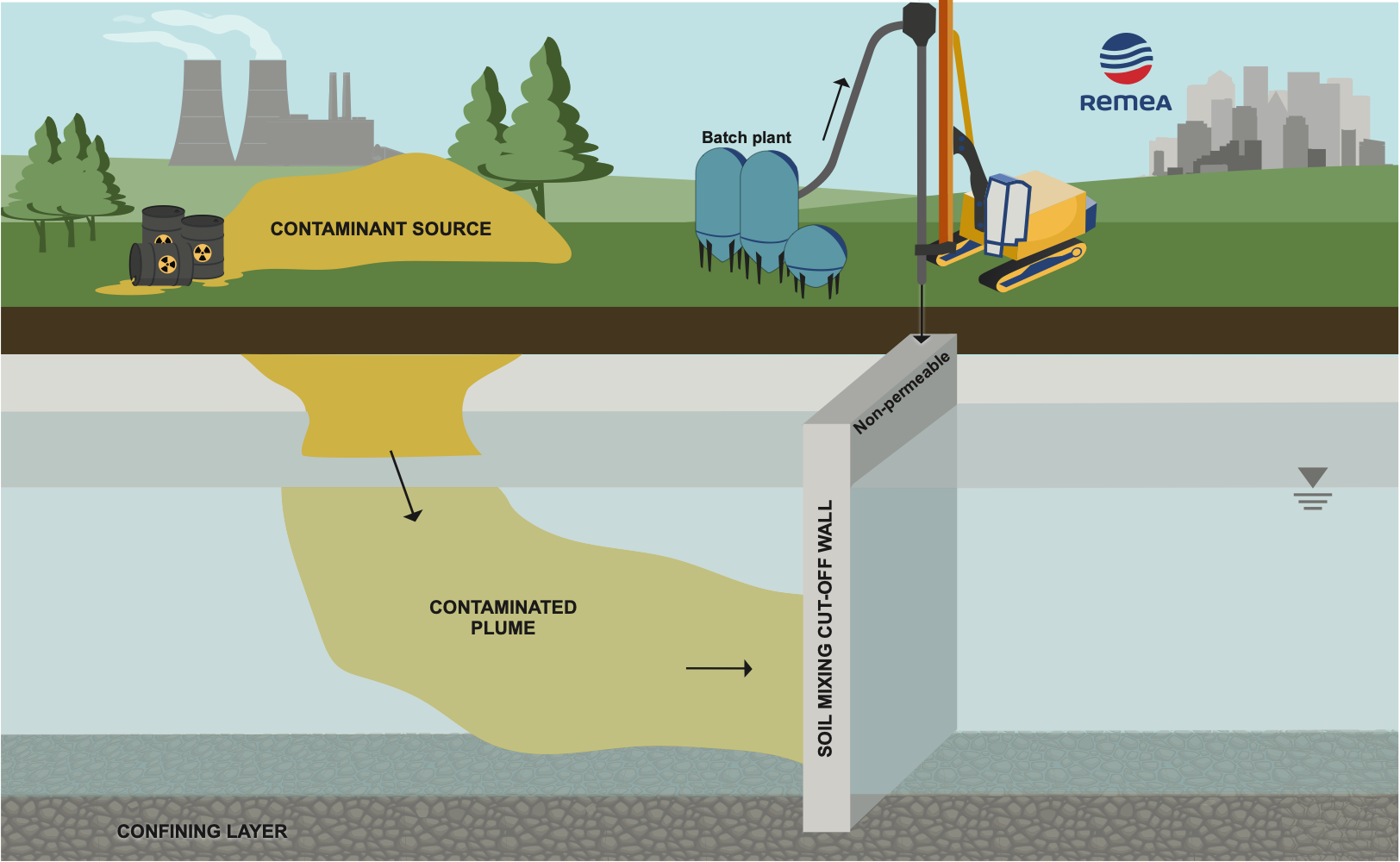
In the context of soil and groundwater remediation, cut-off walls are among the most cost effective in-situ risk mitigation solutions that can be rapidly installed to contain or redirect groundwater contamination in an aquifer. These structures can be made from soil-bentonite, cement-bentonite or soil-cement-bentonite.
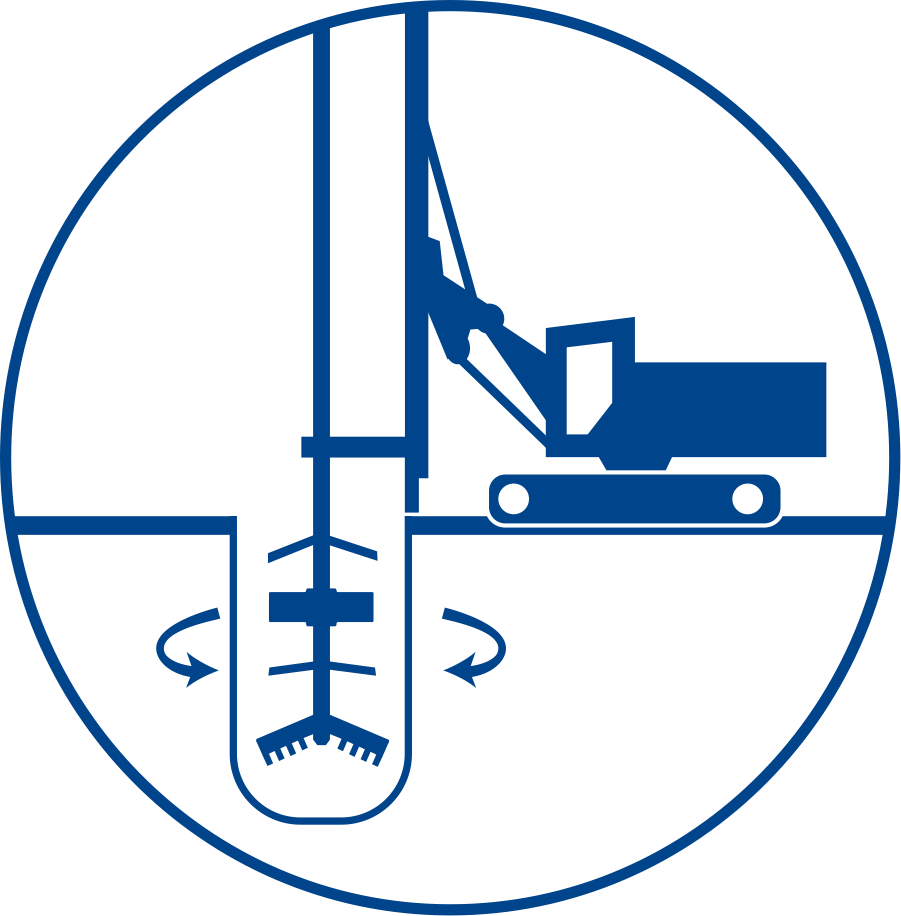
Installation process
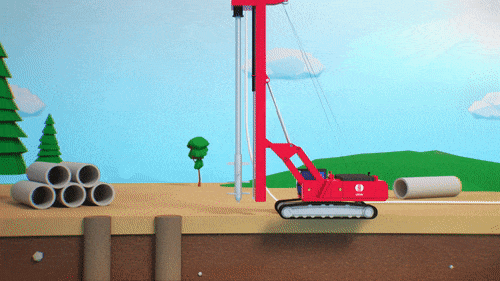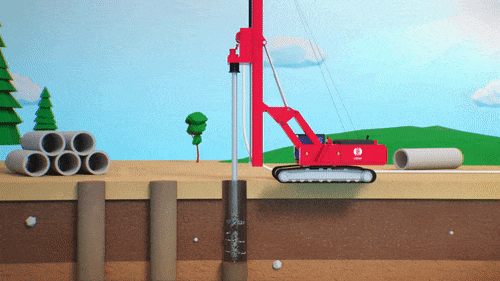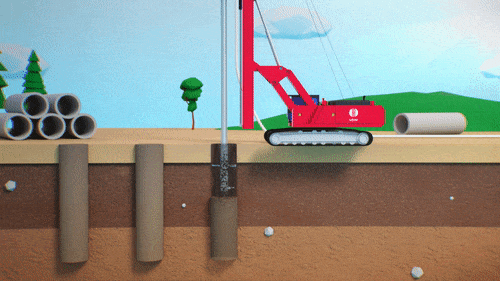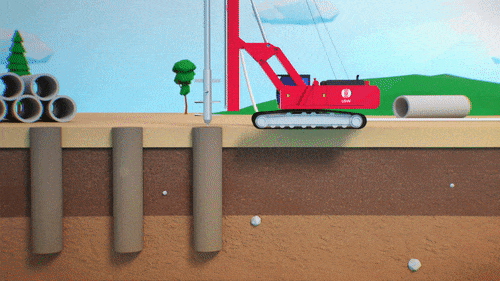
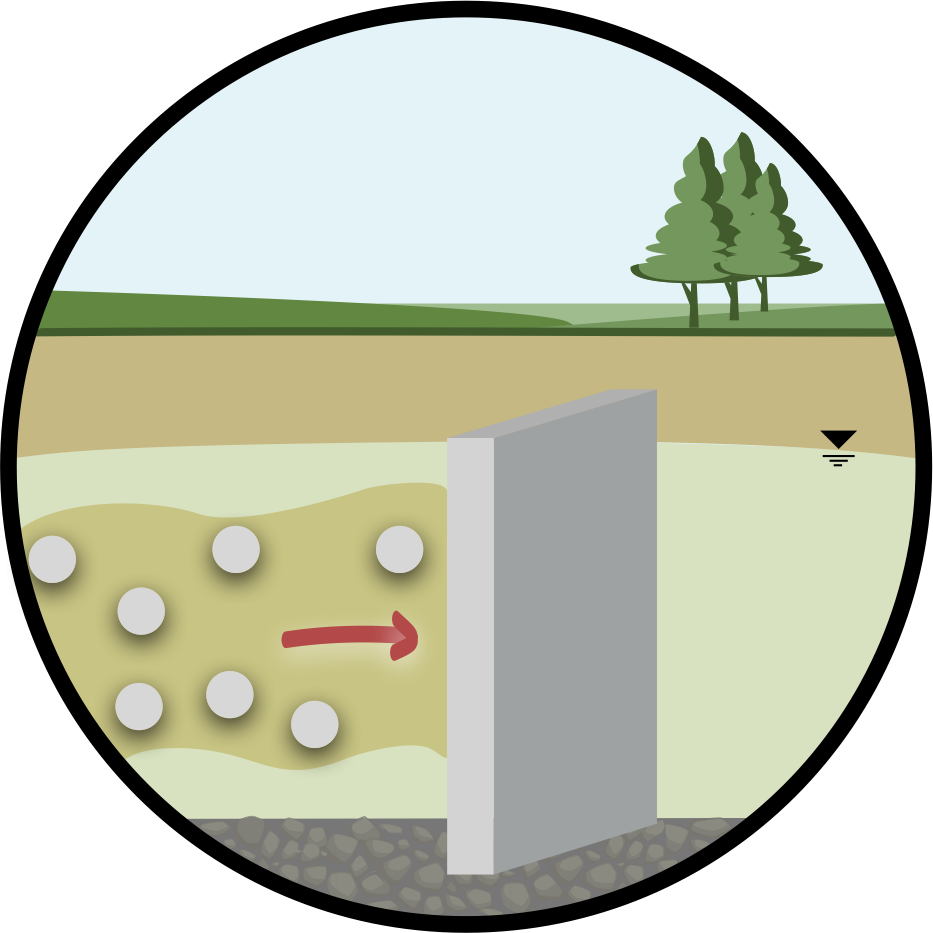
Typically built using a material with a conductivity or permeability of at least one order of magnitude less than the natural material present on site. Since groundwater follows the path of least resistance, cut-off walls are most effective when installed directly on a low permeability confining layer, typically bedrock.
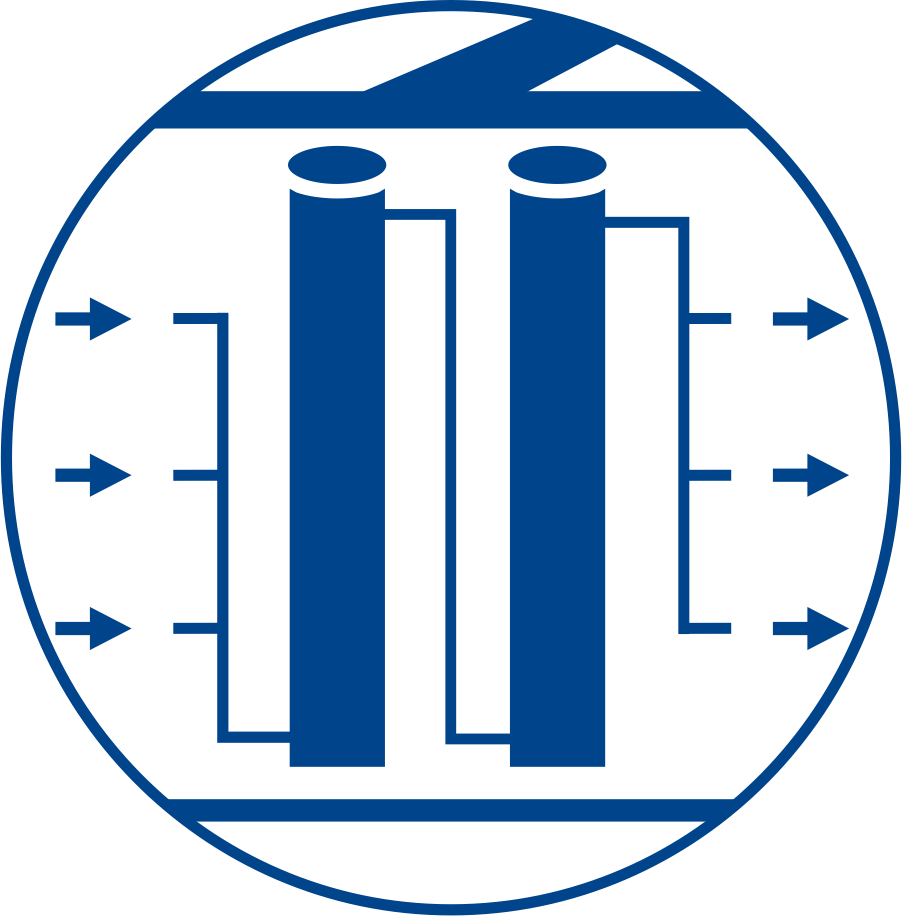
Grid patterns
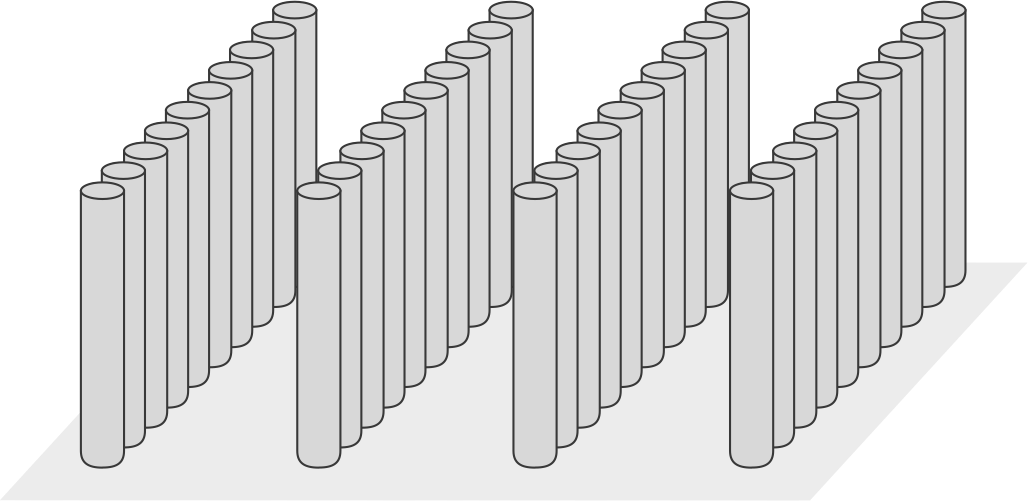
Wall-type
A wall-type installation may be used as a preventative measure to redirect groundwater flow away from a sensitive area. This grid pattern can also be used when installing a serviceable PRB in a “funnel” and “gate” combination.
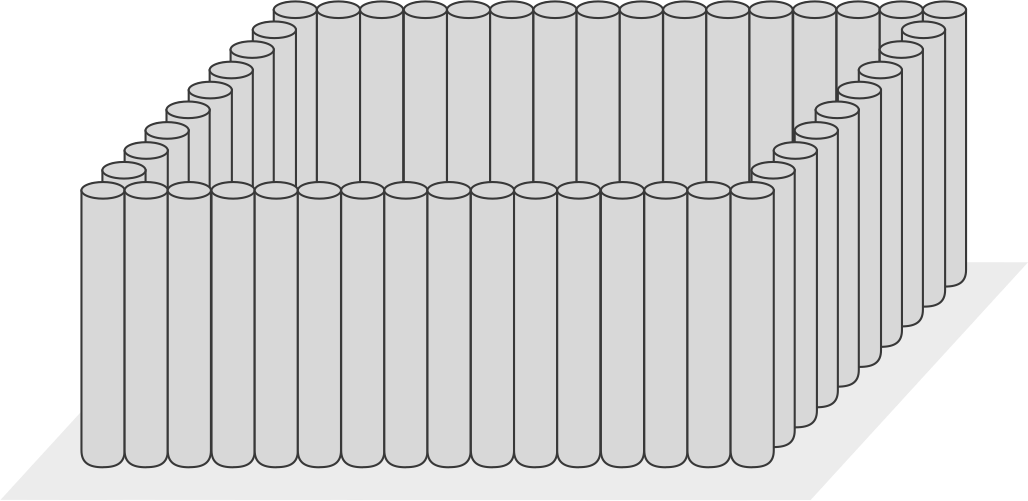
Cellular-type
Also known as in-situ stabilization (ISS), is a preventative measure used to contain (or stop) the spreading of contaminants from the source zone.
Applications
The most watertight and cost-effective method used to install slurry walls include filling an excavated trench with a soil-bentonite or cement-bentonite slurry. Installation depth is limited to the excavator’s boom reach (approx. 25 m) from the excavating surface.
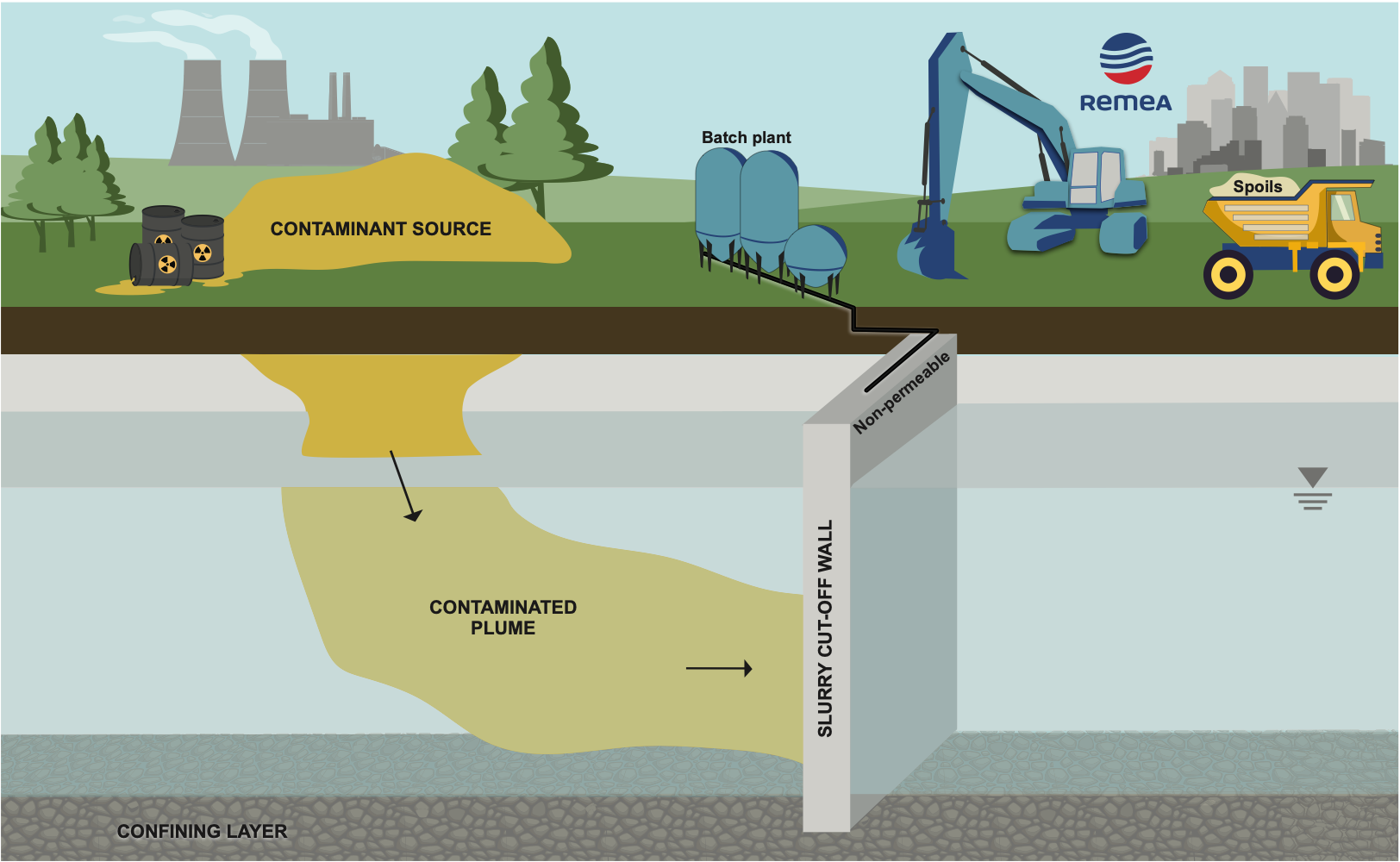
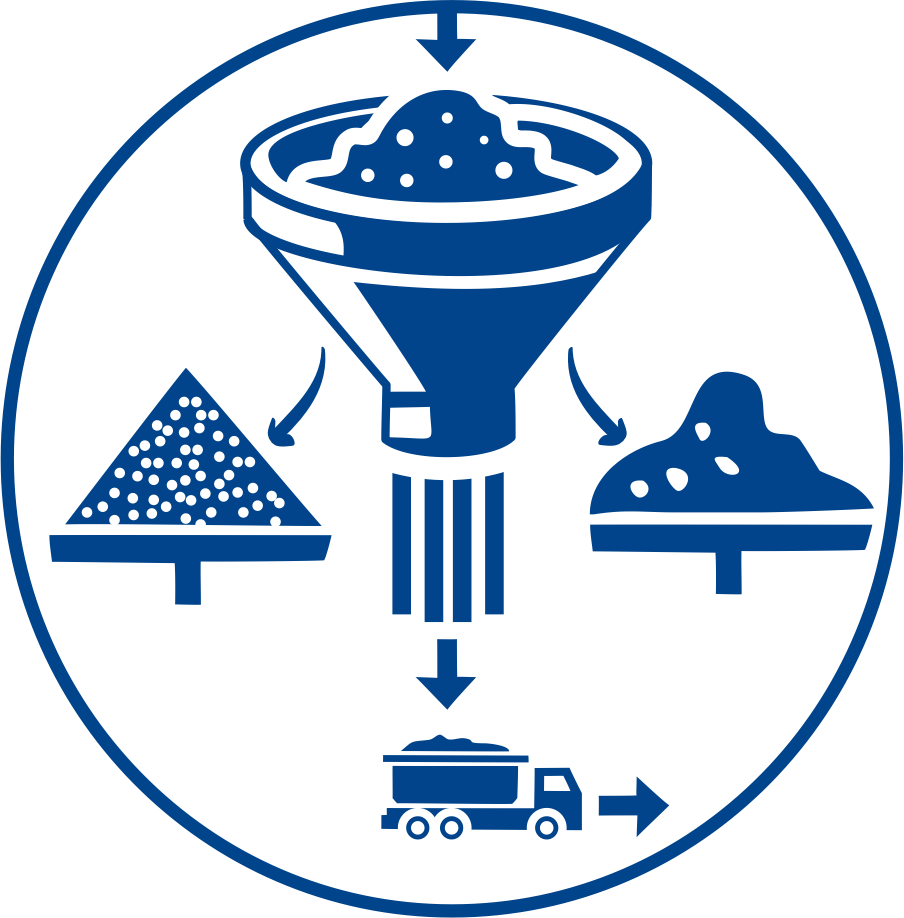
Soil mixing vertical augers in a wall-type grid pattern can also be used to install a slurry cut-off wall by overlapping columns to ensure watertight build. This method generates little surface spoils, ideal to combat Ontario’s new “Excess Soils” regulation. REMEA’s vertical augers can reach depths of 25m.